|
|
Separation of Data and Applications
As described in the feature structured data, the structure of a database
is described through ![]() metadata which is also stored in the database.
metadata which is also stored in the database.
A software application does not need any knowledge about the physical data storage like encoding, format, storage place, etc.
It only communicates with the management system of a database (DBMS) via a standardised interface with the help of a standardised
language like SQL. The access to the data and the metadata is entirely done by the DBMS.
In this way all the applications can be totally seperated from the data. Therefore database internal reorganisations or improvement
of efficiency do not have any influence on the application software.
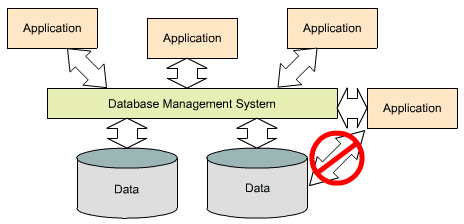 Separation of Data and Applications
Separation of Data and Applications