|
|
What is a Topographic Map?
The International Cartographic
Association defines Topographic Maps as
the following: "Topographic maps are maps at large and medium scales which incorporate a huge variety of information. The basic coverage
(a country’s largest map series) is based on measurements made in the field and/or from aerial photographs. Derived topographical
maps (of medium and small scales ) are prepared by reduction and generalisation from the original basic maps.
(Anson et al. 1984, p. 17)
All components of a topographic map at a specified scale are of equal importance: water, terrain, communication, built-up
areas, vegetation, etc., as well as the lettering of place-names and geographical and cultural features." (Anson et al. 1984,
p. 17)
To simplify matters, we can say that a topographic map is a graphic representation of the three dimensional configuration of the earth’s surface. It shows size, shape and distribution of landscape features, and presents the horizontal and vertical positions of those represented features.
Features on topographic maps can be divided into three major groups:
- Relief: Depicted with brown contour lines that show hills, valleys, mountains, plains, etc. Elevations are given in meters (or feet) above mean sea level. There are also spot elevations (shown in black), where lake level, summit of a hill or road intersections are marked for elevation.
- Water features: Depicted in blue, they represent oceans, lakes, rivers, streams, swamps, etc.
- Cultural features: Depicted in black, they represent all the man-made features: buildings, roads, railroads, land boundaries, etc.
Remark: Topographic maps are distinguished from planimetric maps by the addition of relief in measurable form.
Topographic Map Examples.
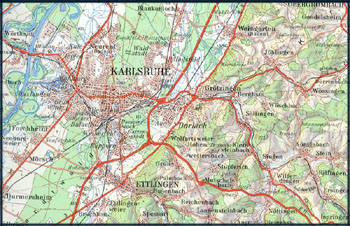
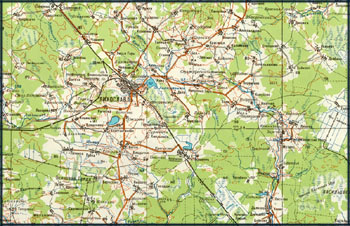
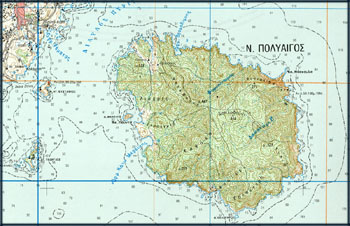
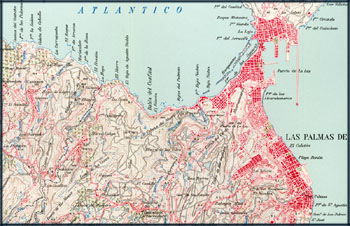
Find below some extracts of topographic maps from different countries.
Observe the difference in colour, typography, detail, etc.
Topographic Map of Germany:
|
Topographic Map of Russia:
|
Topographic Map of Greece:
|
Topographic Map of Spain:
|
Topographic Map of Switzerland:
|