|
|
Spatial pattern and neighborhood of Linear Features
Here we will learn about spatial patterns and neighbourhoods of line features. Especially, how to measure the distance between line features, how to create a buffer polygon or polygons from a line feature and how to create proximal polygons from the line features.
Example of minimum distance calculation from a line feature
Closest distances are calculated using Euclidian distance formula in a similar way to calculating distances between point features, as illustrated above.
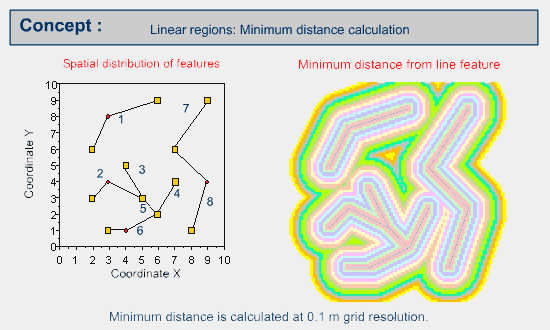
Then the grid cells are allocated based on proximity distance.
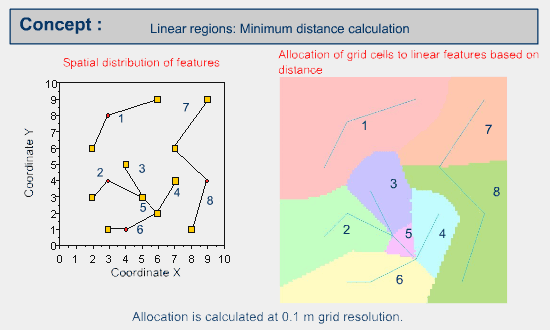
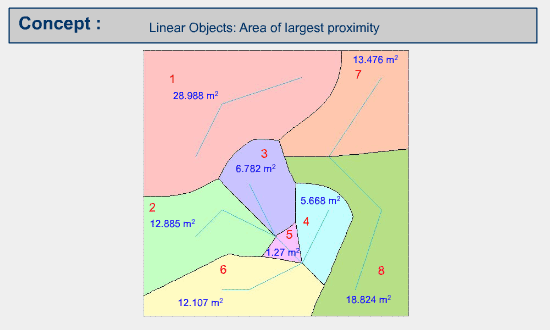
The following figure illustrates the result in vector or object mode.
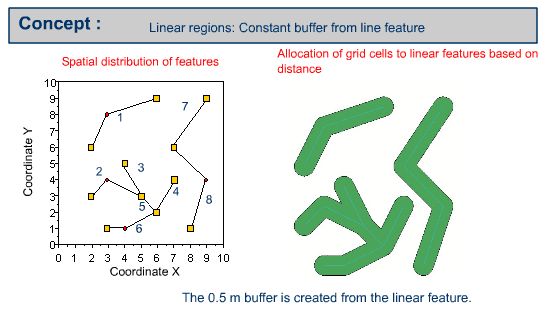
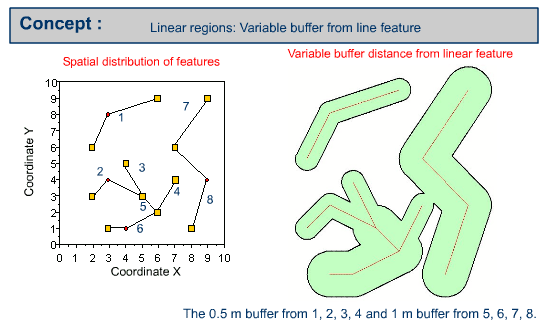
Example of buffering line features
Buffer polygon or polygons can be created by using a constant buffer distance or variable buffer distance around the specified input line feature.
Calculate the minimum distance of line features
- Calculate the closest distance, using the available GIS software from your GIS Lab, based on the line distribution map illustrated. You may choose the resolution of grid cells.
- Then allocate the grid cells to the property of the point feature based on proximity, using the available GIS software from your GIS Lab.
Create Buffers from linear features
- Create the 0.5 meter constant buffer, using the available GIS software from your GIS, Lab based on the linear feature map illustrated.
- Create the 1 m buffer around the linear features 1, 2, 3, and 4 and 0.5 m buffer around the linear features 5, 6, 7, and 8 at the same time, using the available GIS software from your GIS Lab, based on the linear feature map illustrated.
